When I think of healthy foods that are easy to prepare and packed with nutrients, tuna immediately comes to mind. It’s not just a quick lunch fix – tuna is loaded with so many health benefits that make it a standout in the world of nutritious foods. Let’s dive into the specific health benefits of tuna, and how it can make a difference in your overall well-being.
One of the primary health benefits of tuna is its high protein content. Tuna is packed with lean protein, which is essential for muscle growth, tissue repair, and even immune function. A 3-ounce serving of tuna can provide you with about 20 grams of protein, making it a fantastic choice for anyone looking to build or maintain muscle. Whether you’re a busy professional looking for a quick protein boost or someone who loves to hit the gym, tuna can help fuel your body with the essential building blocks it needs. I love how tuna keeps me feeling full for hours, helping me avoid those mid-afternoon snack cravings.
But the benefits don’t end with protein. Tuna is an incredible source of omega-3 fatty acids, those healthy fats that are essential for heart health. Omega-3s have been linked to reduced risk of heart disease, lower blood pressure, and decreased inflammation. It’s amazing to think that something as simple as adding tuna to your diet could have such a profound effect on heart health. I try to eat tuna regularly to make sure I’m getting enough omega-3s – they’re so important, especially as we age. Not only do omega-3s help protect the heart, but they’re also great for brain health, improving cognitive function, and even supporting mental well-being.
Tuna’s Impact on Weight Management
Weight management can be a tricky topic, but the nutritional value of tuna makes it a great ally in the battle to maintain a healthy weight. Since tuna is low in calories yet high in protein, it’s the perfect food to incorporate into your meals if you’re watching your weight. A 3-ounce serving of tuna has only around 100 calories, which makes it a guilt-free, satisfying option. I’ve found that incorporating tuna into my meals helps me stay full for longer without the calorie overload.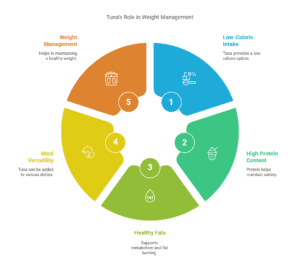
Tuna also contains a modest amount of healthy fats, which can help support metabolism and fat burning. These fats, especially the omega-3s, play a role in regulating insulin levels and enhancing fat oxidation. And let’s not forget that tuna is versatile – you can add it to a variety of dishes like salads, wraps, or even tuna bowls. It’s an easy way to make a meal feel more substantial without piling on extra calories. For me, having a few servings of tuna each week keeps me on track with my weight management goals, all while ensuring I’m eating something nutritious.
Here’s a look at the nutrition of tuna in terms of calories and fat:
| Nutrient | Amount per 3 oz Serving |
| Calories | 100 kcal |
| Total Fat | 1 gram |
| Saturated Fat | 0 grams |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0.5 grams |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 0.5 grams |
By replacing higher-calorie, higher-fat options with tuna, you’re making a smart choice that’s not just about cutting calories, but also about nourishing your body with the right nutrients. Tuna provides the satisfaction of a meal that will fill you up without weighing you down.
Tuna’s Role in Supporting Heart Health
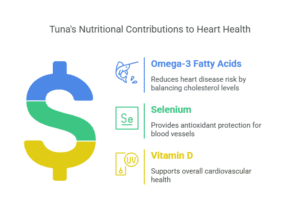
If there’s one thing I’ve learned over the years, it’s that heart health is something we should all take seriously. A healthy heart keeps everything else in our body running smoothly, and thankfully, the nutritional value of tuna can support that in a big way. As I mentioned earlier, tuna is a fantastic source of omega-3 fatty acids. These fats have been shown to help reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering bad cholesterol levels (LDL) and raising good cholesterol levels (HDL).
Adding tuna to your diet regularly can also help maintain a healthy blood pressure. Omega-3s found in tuna work to relax blood vessels and reduce inflammation, which can help keep blood pressure levels in check. This is one of the reasons I try to include tuna in my meals a few times a week – it’s such a simple way to take care of my heart.
What’s more, tuna contains a significant amount of selenium, a mineral that is known for its antioxidant properties. Selenium helps protect the cells of the body from oxidative stress, which can damage blood vessels and contribute to heart disease. Just a 3-ounce serving of tuna provides about 30% of your daily recommended intake of selenium, which makes tuna an excellent choice for promoting cardiovascular health.
Here’s a quick overview of tuna’s heart-healthy nutrients:
| Nutrient | Amount per 3 oz Serving |
| Omega-3s | 1,000 mg |
| Selenium | 30% of Daily Value |
| Vitamin D | 10% of Daily Value |
By including tuna in your diet, you’re not just enjoying a delicious meal – you’re taking proactive steps to maintain a healthy heart. And as I always say, the heart is the true engine of the body. Keeping it well-fed with the right nutrients is one of the best things we can do for our long-term health.
Tuna for Healthy Skin and Hair
As someone who is always looking for ways to improve my skin and hair, I’ve found that tuna is a game-changer. The nutritional value of tuna extends beyond just muscle and heart health; it also provides essential nutrients that support skin and hair health. Vitamin D, which is abundant in tuna, helps protect against skin damage and supports the body’s ability to repair itself. Plus, the omega-3 fatty acids found in tuna help keep the skin moisturized, preventing dryness and flakiness.
But it’s not just about moisturizing – tuna also provides a boost to collagen production. Collagen is the protein that keeps our skin firm and elastic. By eating tuna, I’m giving my skin the tools it needs to stay youthful and radiant. Omega-3s also play a role in preventing wrinkles and promoting healthy hair growth. If you’ve been struggling with dry, brittle hair, I highly recommend adding tuna to your diet. In my own experience, I’ve noticed that when I regularly consume tuna, my hair feels thicker and shinier, and my skin stays soft and glowing.
So, if you’re looking for an easy and delicious way to support healthy skin and hair, look no further than a tasty tuna meal. Whether in a salad, a sandwich or as a side dish, the benefits are well worth it.
The Versatility of Tuna in Your Diet
I love the versatility of tuna and let me tell you, it’s a game-changer when it comes to meal planning. Whether I’m looking to whip up something quick for lunch, add some protein to a salad, or prepare a hearty dinner, tuna is always on the menu. The best part? The nutritional value of tuna ensures that no matter how you prepare it, you’re getting a healthy, satisfying meal.
Tuna is one of those foods that’s incredibly adaptable. You can enjoy it in a salad, toss it into pasta, or even throw it on a sandwich. I’ve made everything from tuna melts to simple tuna bowls, and each time I’m blown away by how much flavor it packs. The high protein and low-calorie nature of tuna makes it the perfect base for a healthy meal. Whether you prefer the classic tuna salad, or you’re feeling adventurous with a tuna poke bowl, this fish can elevate any dish. It’s one of those foods that feels like a quick fix but offers long-term nutritional benefits.
Another great way to enjoy tuna is as a snack. I love taking a can of tuna, draining it, and mixing it with a little bit of Greek yogurt, mustard, and diced pickles for a satisfying, low-calorie dip. It’s simple, delicious, and helps keep my energy levels up during those mid-afternoon slumps. And let’s not forget tuna sushi rolls – who says healthy can’t be delicious and fun to make? I find that tuna’s versatility is one of the key reasons why it’s such a staple in my diet, whether I’m at home or at work.
Tuna can also be a great addition to meal prep. If you’re someone who likes to plan ahead for the week, having tuna on hand makes it easy to create quick, healthy meals. You can portion it out into containers, pair it with veggies, or even serve it on top of quinoa or rice for a balanced, nutrient-packed meal. For me, it’s an absolute lifesaver on busy days when I want something quick but still healthy.
How to Choose the Right Tuna for Maximum Nutrition
When it comes to choosing the right tuna, the type of tuna you pick makes a difference in the nutritional value of tuna. You’ve probably seen cans of tuna labeled as “in water” or “in oil.” I always go for the one packed in water because it’s much lower in fat and calories. Tuna packed in oil can be delicious, but it contains more calories and unhealthy fats. By choosing tuna packed in water, you can enjoy all the health benefits without the extra calories.
Another thing I consider when choosing tuna is whether it’s wild-caught or farmed. Wild-caught tuna tends to be leaner and often contains higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which is one of the biggest reasons I include tuna in my diet. Omega-3s are essential for heart health, brain function, and reducing inflammation, so the more of them, the better! I’ve personally noticed that wild-caught tuna has a firmer texture and a richer flavor, which is why I lean toward it when making my meals.
In addition to water-packed, wild-caught tuna, I also look for brands that are sustainably sourced. Overfishing is a real issue, and I want to make sure that I’m supporting companies that are taking the necessary steps to ensure tuna populations remain healthy for future generations. While it might be a little pricier, I find that investing in high-quality, sustainably sourced tuna is worth it for both the environment and my health. It’s always great to know that my meals are supporting a more sustainable future.
Here’s a breakdown of tuna varieties to consider for the best nutritional value:
| Type of Tuna | Calories (per 3 oz) | Omega-3 (per 3 oz) | Protein (per 3 oz) |
| Tuna in Water | 100 kcal | 1,000 mg | 20 grams |
| Tuna in Oil | 200 kcal | 800 mg | 20 grams |
| Wild-Caught Tuna | 90 kcal | 1,200 mg | 20 grams |
By making small adjustments to the type of tuna you buy, you can maximize the health benefits it offers. Wild-caught tuna in water will give you the best of both worlds – low calories, high protein, and a solid boost of omega-3s.
How to Store Tuna for Maximum Freshness and Nutritional Value
Storing tuna properly is just as important as choosing the right kind. If you’re anything like me, you probably buy canned tuna in bulk, especially when it’s on sale, and want to make sure it stays fresh. Thankfully, tuna is one of those foods that has a long shelf life when stored correctly. Canned tuna typically lasts for 2-5 years when kept in a cool, dry place. That means I can stock up and always have a quick meal on hand without worrying about it going bad.
Once you open a can of tuna, though, the clock is ticking. I always recommend transferring any leftover tuna into an airtight container and storing it in the fridge. Properly stored, opened tuna will stay fresh for 1-2 days. If you want to extend the freshness even further, you can also freeze tuna, although I find it’s best consumed fresh after opening. I try to keep my meals simple and enjoy the tuna within the same day, especially because that’s when the flavor and nutritional value are at their peak.
For cooked tuna dishes like tuna salad, I recommend eating them within 1-2 days for the best taste and nutritional content. This is particularly important if you’ve mixed in ingredients like mayonnaise or yogurt, which can spoil faster. To ensure your meals are always fresh, I often make just enough tuna salad or tuna bowls for the day and avoid letting it sit in the fridge for too long. It’s all about keeping it fresh, so you can enjoy the full nutritional value of tuna.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the health benefits of eating tuna?
Tuna is packed with nutrients that are great for your health. It’s a rich source of high-quality protein, making it an excellent choice for muscle repair and overall body function. Tuna is also loaded with omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health, reduce inflammation, and enhance brain function. Plus, it’s low in calories, making it an ideal choice for those looking to maintain a healthy weight or reduce their fat intake.
Is tuna good for weight loss?
Yes, tuna is an excellent food for weight loss. With its high protein content and low-calorie count, it helps keep you full for longer, reducing the urge to snack between meals. Protein also supports muscle mass, which is key when you’re working toward a leaner body. Just be mindful of how you prepare it—adding too much mayo or dressing could increase the calorie content.
Can I eat tuna every day?
While eating tuna every day can be a great source of protein and omega-3s, moderation is key. Due to its mercury content, it’s recommended to limit your intake to around 2-3 servings per week, especially for pregnant women or young children. As long as you vary your protein sources, incorporating tuna regularly into your diet can be part of a healthy eating plan.
Is canned tuna healthier than fresh tuna?
Canned tuna and fresh tuna both offer similar nutritional benefits, including high protein and omega-3 fatty acids. The main difference lies in the freshness and processing methods. Fresh tuna may have a slightly better texture and flavor, but canned tuna is convenient, affordable, and lasts much longer. Just be mindful of the added ingredients in canned varieties, such as oil or salt.
How can I make tuna taste better?
Tuna is incredibly versatile, and there are endless ways to make it taste even better! You can mix it with Greek yogurt, mustard, or a squeeze of lemon juice to add creaminess and tang. For extra flavor, add fresh herbs like dill or parsley, and don’t forget to throw in some crunchy veggies like pickles, celery, or red onions. The key is to experiment with different ingredients to find your favorite combination!
conclusion
the nutritional value of tuna makes it an exceptional choice for anyone looking to add a healthy, protein-packed option to their diet. Whether you prefer canned or fresh tuna, the variety it offers in taste, texture, and preparation options is something I truly appreciate. From quick meals like tuna salad to more elaborate dishes like sushi or tuna melts, this fish is incredibly versatile and full of health benefits.
Tuna not only supports heart and brain health but also aids in muscle growth, making it a perfect food for active individuals. Plus, with its low-calorie content, it’s great for weight management and offers a satisfying meal without adding excessive calories. If you haven’t already, I highly recommend incorporating tuna into your meals regularly, but remember to choose wisely—opt for water-packed, wild-caught tuna for the best nutritional benefits.
As we wrap up, consider how you can make tuna a staple in your weekly meal plan. There are so many easy ways to incorporate it, whether you’re looking for a simple lunch or preparing a more complex dinner. So go ahead, grab a can of tuna, get creative, and start enjoying the amazing benefits it has to offer. Stay healthy, stay strong, and don’t forget to experiment with your favorite recipes!